poultry monitoring
-
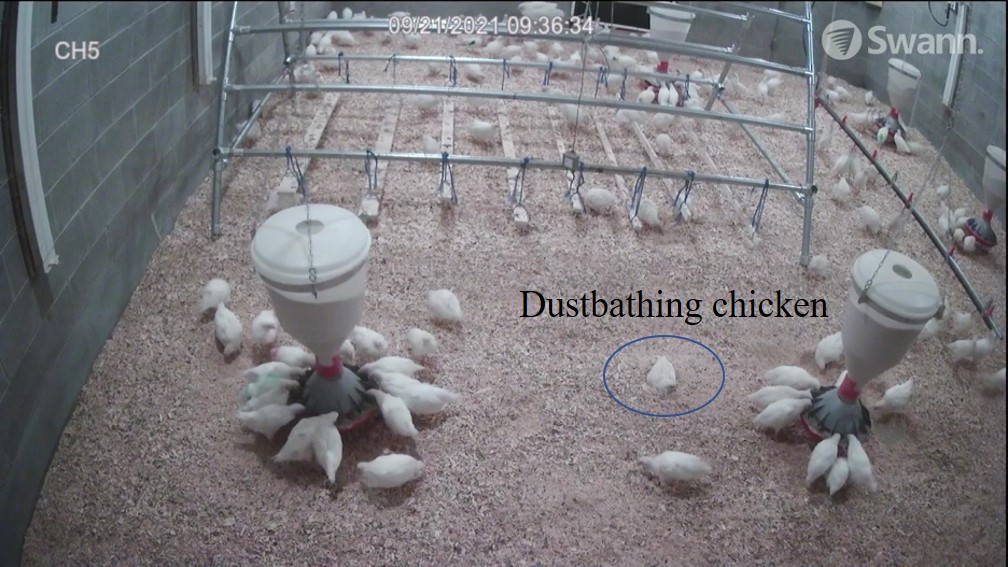

The U.S. laying hen industry is transitioning from conventional caged (CC) systems to cage-free (CF) housing as driven by concerns of animal welfare, promoted by public demand for improved conditions and natural behavior among laying hens such as dustbathing (DB). The DB is a functionally important maintenance behavior in birds that clean plumage, realigns feather…
-
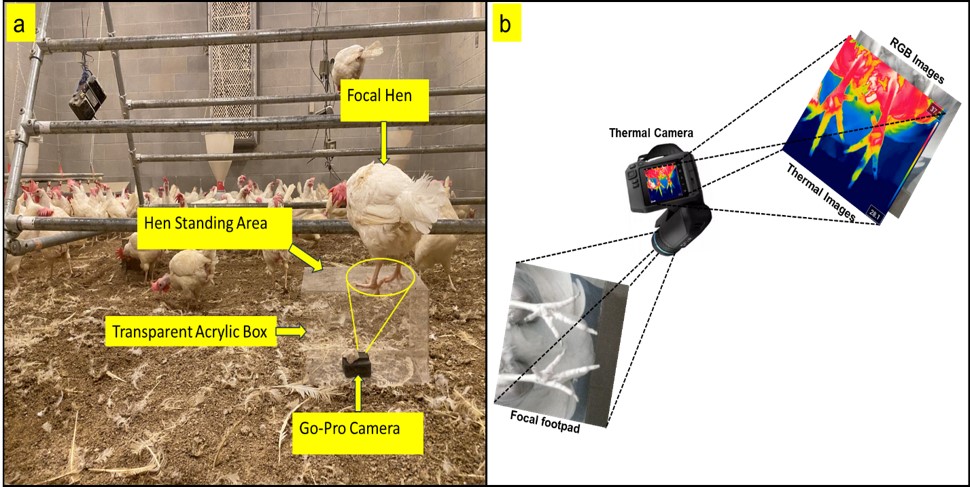
Footpad dermatitis (FPD) is a common poultry condition that can negatively influence chickens’ production, welfare, and health. FPD also called pododermatitis, is a widespread condition affecting broilers and laying hens. It is characterized by the development of inflammatory lesions, ulcers, and necrotic tissue on the plantar surface of the chickens’ feet. The FPD condition is…
-

As global demands on the poultry production and welfare both intensify, the precision poultry farming technologies such as computer vision-based cybernetics and robotic system is becoming important in addressing the current issues related to animal welfare and production efficiencies. The integration of computer vision technology has become a catalyst for transformative change in precision farming,…
-

Animal activities and behaviors provide significant insights into the mental and physical well-being of poultry, serving as a key indicator of their health and subjective states. For instance, predicting indoor particulate matter concentration in poultry houses can be informed by broiler activity and ventilation rates. Additionally, locomotor activity acts as a proxy for the gait…
-

In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) advancements have greatly influenced the agricultural industry, particularly with the emergence of large foundation models. One such model, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) developed by Meta AI Research, has revolutionized object segmentation tasks. SAM has a revolutionary object segmentation utility by employing a cutting-edge foundation model. SAM demonstrates extraordinary…
-

Bumblefoot (pododermatitis, footpad dermatitis, or foot rot) is the term used to describe a common bacterial infection and chronic inflammatory reaction in a chicken. It is clinically characterized by swelling, abrasion, hyperkeratosis, and ulceration of the digital pad, planta metatarsal region, or both. Bumblefoot compromises the foot’s internal tissues, including the mesoderm, tendons, and bones,…
-

Broiler body weight monitoring is critical for evaluating the growth and performance of a flock. The obtained bodyweight and uniformity of the flock are indicators of daily growth rate, feed-to-meat conversion ratio, health conditions, and marketing day prediction. The traditional protocol is to manually sample and weigh a certain ratio of a flock one by…
-

Introduction For commercial broiler production, about 20,000 – 30,000 birds are raised in each confined house, which has caused growing public concerns on animal welfare. Currently, daily evaluation of broiler wellbeing and growth is conducted manually, which is labor intensive and subjective to human errors. Therefore, there is a need for an automatic tool to…
-
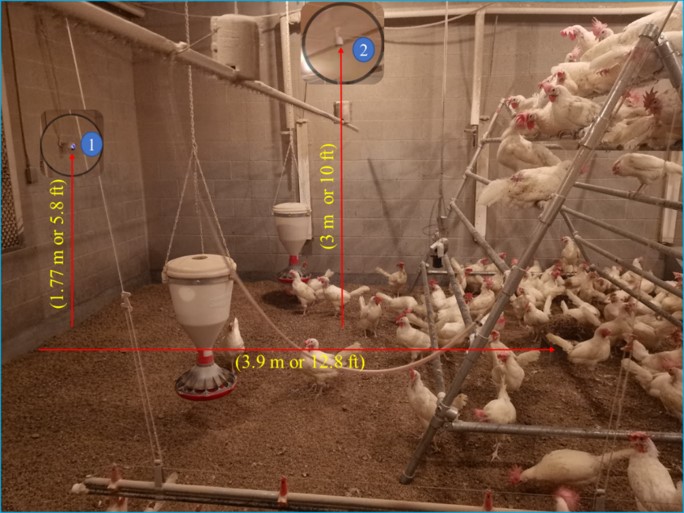

Introduction The spatial distribution of laying hens in cage-free houses is an indicator of flock’s health and welfare. While larger space allows chickens to perform more natural behaviors such as dustbathing, foraging, and perching in cage-free houses, an inherent challenge is evaluating chickens’ spatial distribution (e.g., real-time birds’ number on perches or in nesting boxes).…
-

Introduction While CF house allows hens to perform more natural behaviors (e.g., dust bathing, perching and foraging on the litter floor), a particular challenge is floor eggs (i.e., mislaid eggs on litter floor). Floor eggs have high chances of contamination. The manual collection of eggs is laborious and time-consuming. Delayed floor egg collection may lead…