poultry monitoring
-

The poultry industry faces growing challenges in ensuring animal welfare, preventing disease outbreaks, and addressing labor shortages. Traditional vision intelligence-based behavior monitoring needs intensive manual labeling, which is impractical for large-scale operations, necessitating advanced, efficient, and scalable solutions. Utilizing artificial intelligence technologies to monitor poultry behavior accurately in real-time can revolutionize animal welfare practices and…
-
U.S. egg production is shifting from conventional caged systems to cage-free systems, largely due to growing concerns about animal welfare. Over the past decade, the market share of non-organic cage-free eggs has increased by 5–10%, reaching 40% by 2025. However, cage-free housing is associated with higher rates of mortality and injury, often linked to poor…
-

The UGA Poultry Science Extension team just hosted a successful 2025 Georgia Layer Conference at the GPLN in Gainesville, GA on September 22, 2025. We sincerely thank all the speakers for sharing valuable updates and insights on key topics such as laying hen production, the transition to cage-free systems, egg safety, avian influenza outbreaks, mite…
-
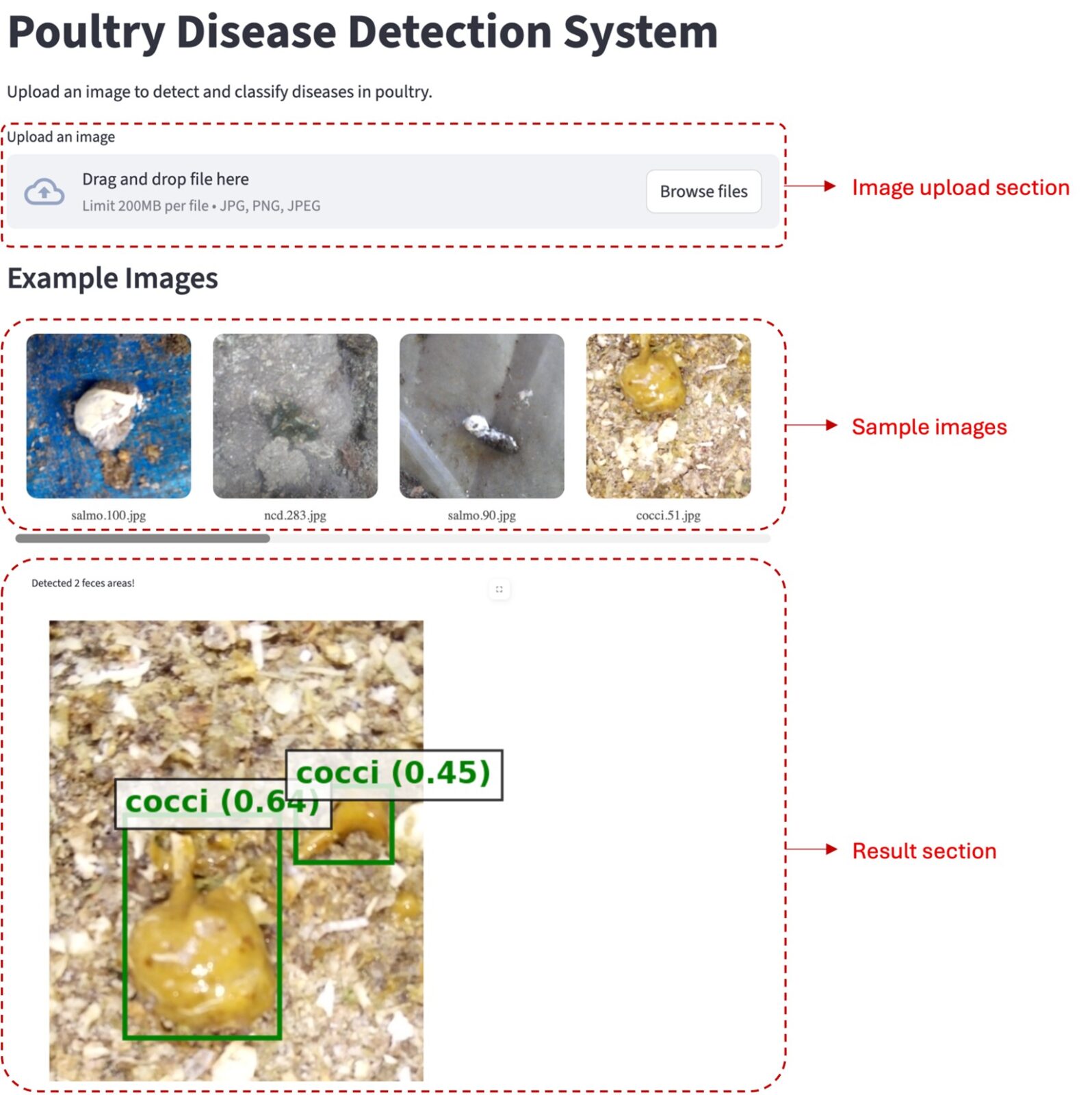
In modern poultry production, thousands of chickens are raised in a confined housing system, which tends to have animal disease or well-being issues. Early disease detection is essential to limit spread and economic loss. Poultry diseases threaten animal welfare and productivity, especially in cage-free systems where communal environments increase disease transmission risks. Traditional diagnostic methods,…
-
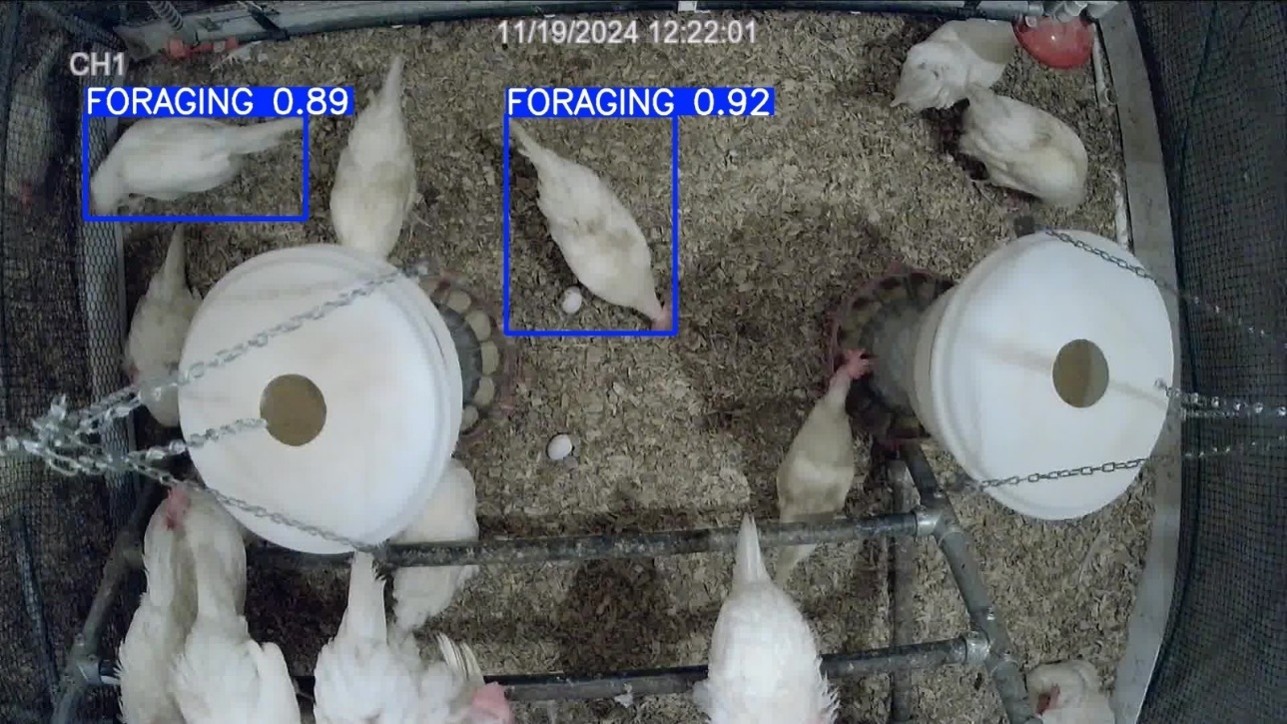
Foraging is considered one of the most important natural habits in chickens, as they spend a significant portion of their time doing it (Figure 1). US egg production is shifting from conventional caged system to cage-free production considering the hens will have more freedoms in performing natural behaviors such as dustbathing and foraging. Foraging behavior…
-
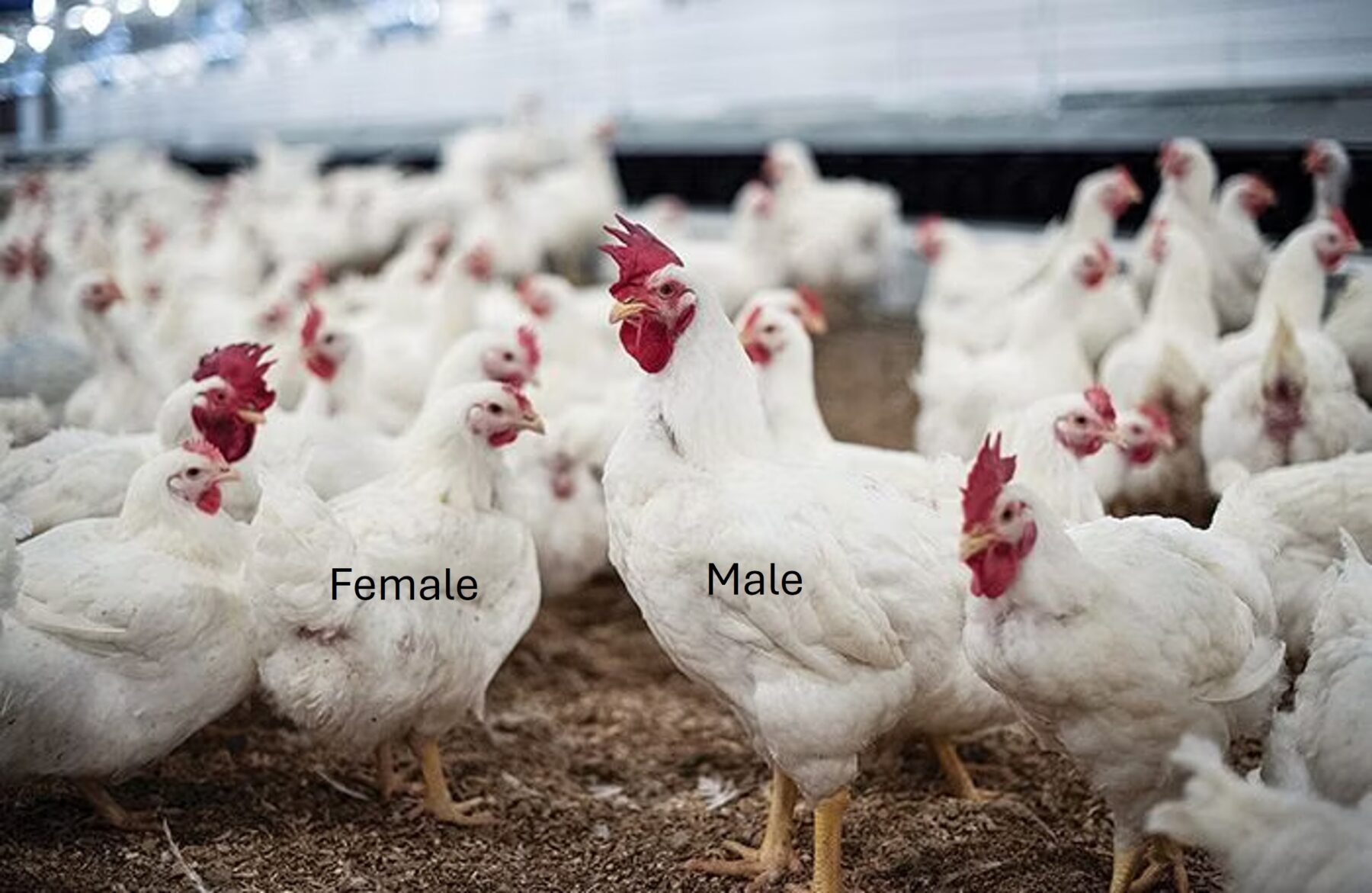

Roosters’ behavior and activity are critical for egg fertility and hatchability in broiler or layer breeder houses. Desirable roosters are expected to have a good leg health, reach sexual maturity, be productive, and show less aggression to females during mating. However, not all roosters are desirable and low productive roosters should be removed for replacement.…
-
Poultry behaviors such as drinking and feeding are critical for evaluating animal welfare and health. In commercial poultry houses, there are thousands of chickens in a flock, which makes monitoring individual behavior such as drinking and feeding challenging. In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly impacted agriculture, particularly with the development of deep learning…
-
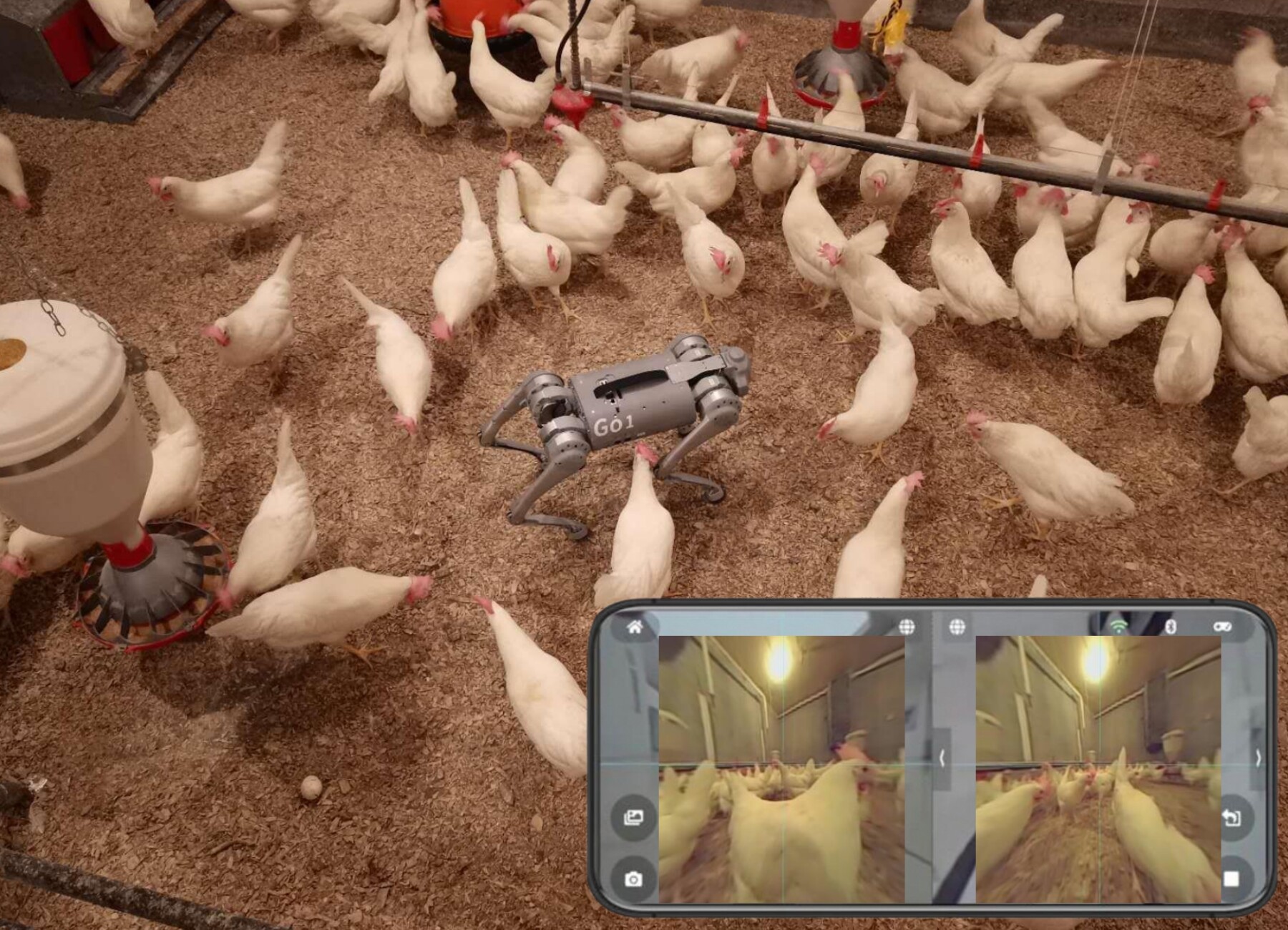

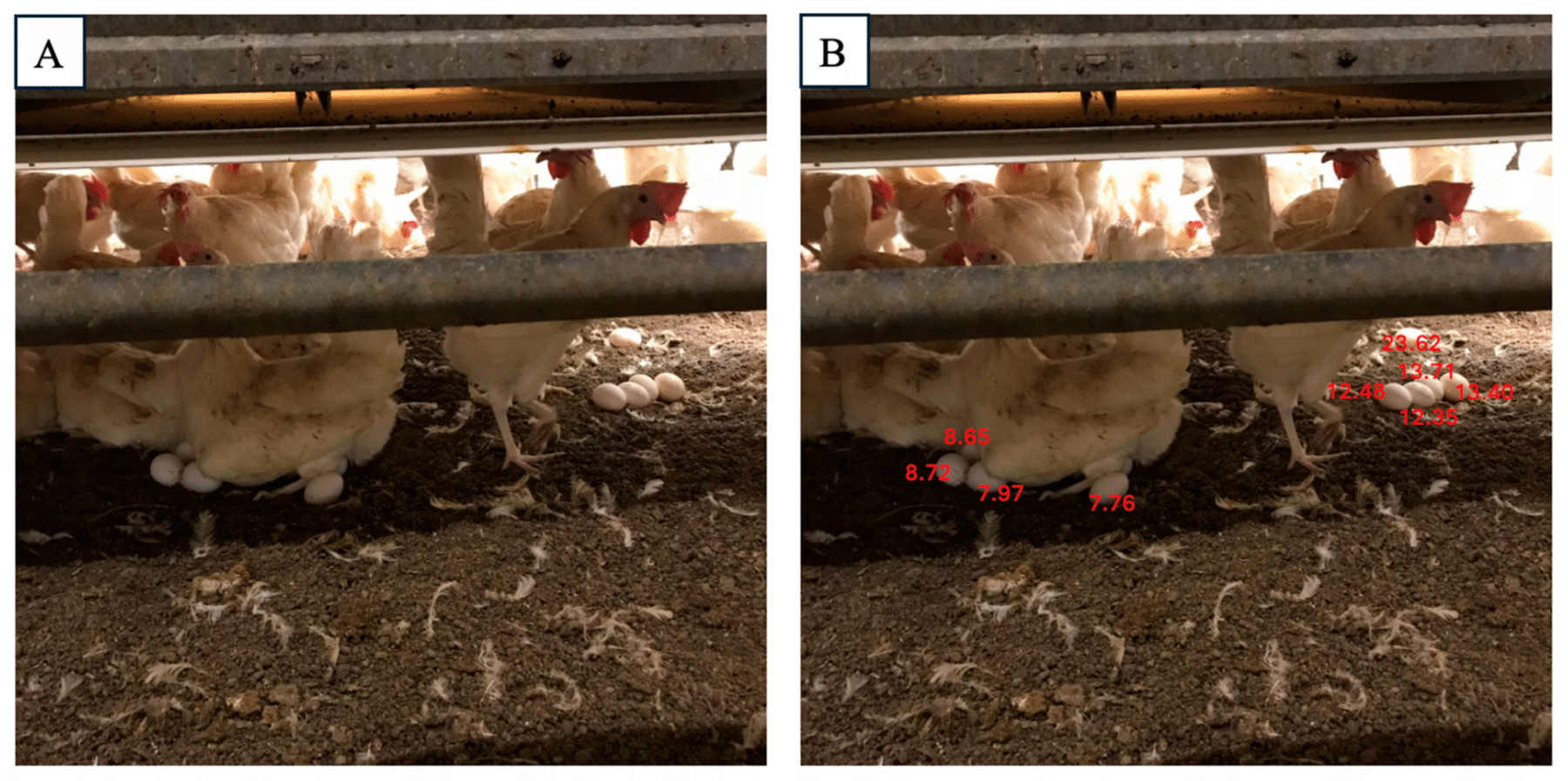
It’s estimated that approximately 20 million chickens in the U.S. die in commercial poultry houses before reaching market age or arriving at slaughterhouses for various reasons. In commercial broiler or cage-free laying hen houses, thousands of chickens are housed within the same facility in high density. Animal wellbeing monitoring, including daily mortality checks, is typically…
-
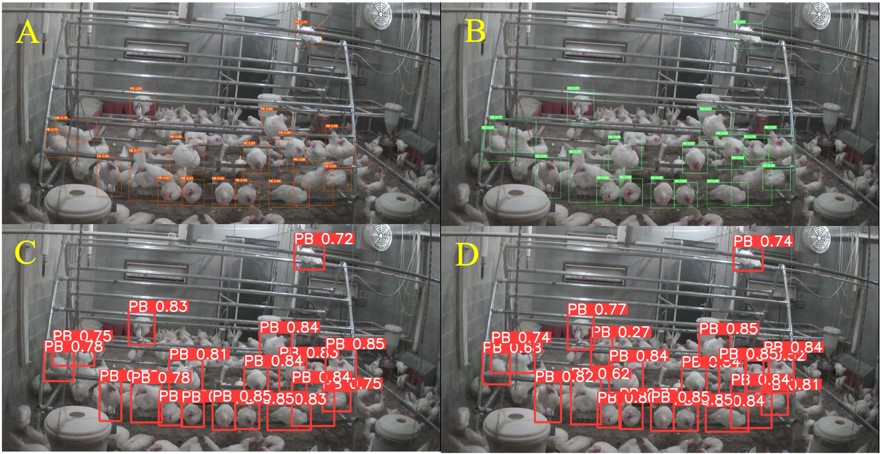

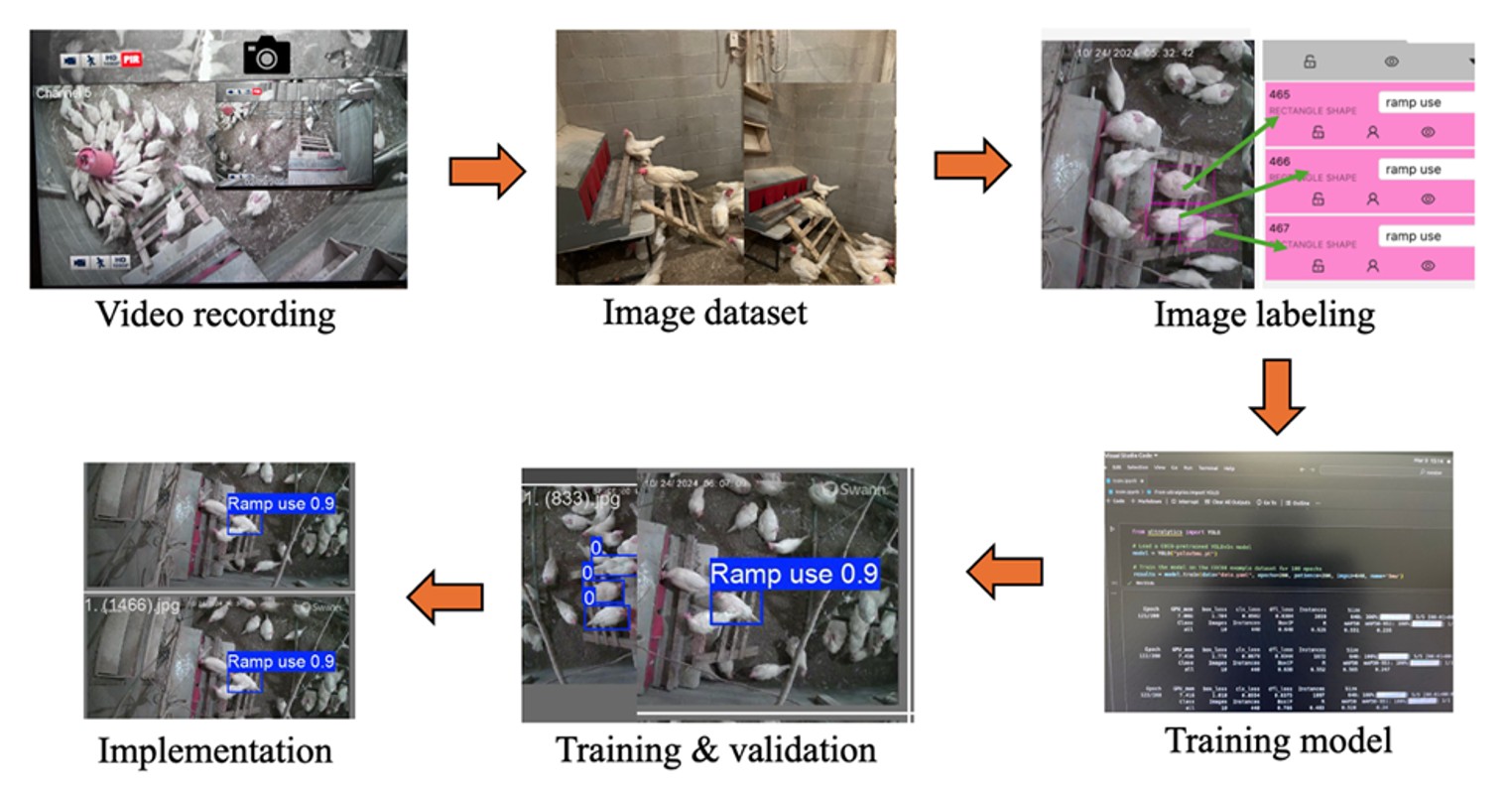
Domestic fowl shows the tendon-locking phenomenon, which lets them to express perching behavior (PB) with minimum muscular effort. The domestic hens look for an elevated structure for resting during night as that the jungle fowl, in order to prevent themselves from ground predators. Providing perches in cage-free (CF) housing (Figure 1) offers significant benefits for…
-
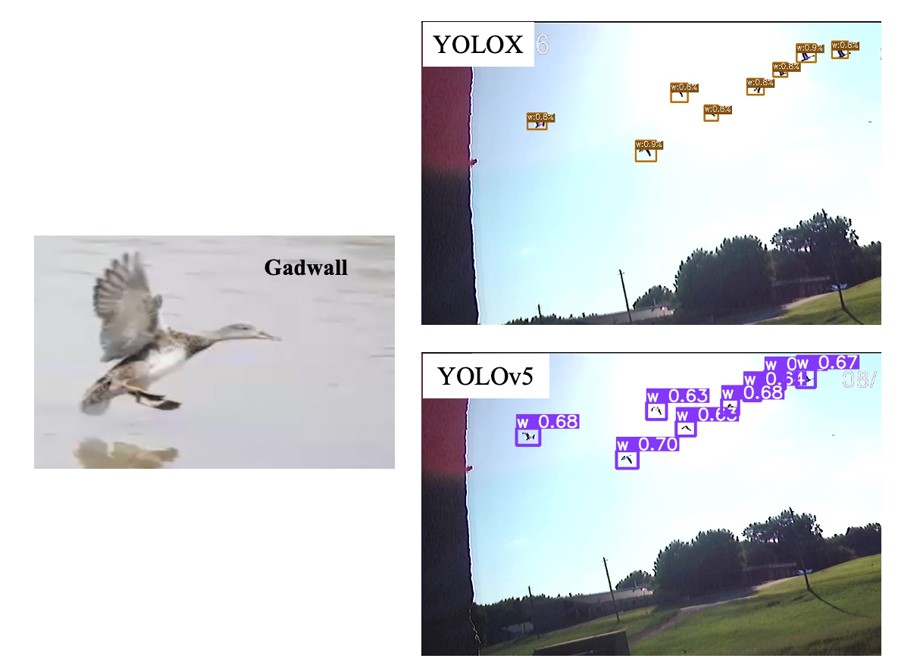

High pathogenicity avian influenza (HPAI) is disastrous for poultry industries worldwide. The outbreak of HPAI in 2014-2015 caused the loss of 60 million chickens and turkey, and the most recent HPAI outbreak since 2021 has led to losses of over 100 million chickens so far in the US. Farm biosecurity management practices have been applied…